Skin Worksheets
Human Skin Lesson Plans From MatchCard Science
The human skin worksheets are from the MatchCard Science Human Anatomy Unit Study
for grades 3 - 8.
Free Download Below
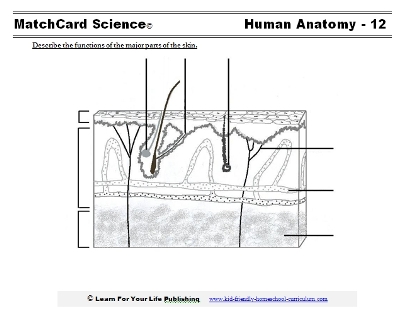

Download and Use the Human Skin Worksheets
This is MatchCard #12 of the Human Anatomy Unit Study. This three page pdf includes the student worksheet, the teacher's answer key, and information pieces for students to place on their copy.More information below on MatchCard Science Unit Studies.
You're Covered in Skin
Hands-on Activities and projects for human skin
Magnifying Glass
Let students examine their own skin with a magnifying glass.Compare the skin surfaces of:
- the back of their hand
- the palm
- finger prints
It Rubs Me The Wrong Way
Here's an interesting way to experience that famous saying.Have a student close their eyes (or blindfold them if the temptation to peek is strong.)
They place both arms outstretched on a table in front of them - palms down.
Use a small index card or other firm flat object.
Run the card over their skin in the direction from their hands toward their shoulders. The card should be close enough to the skin to touch the hairs, but far enough it does not touch their skin.
The student states when they feel something and describe what they feel. Insist that you did not touch their skin.
Why could they feel it? (Answer, hair follices go through the epidermis.)
Explain the value of hair. When it stands straight up the hair follicles trap a small amount of hair that is warmed by your body heat. You have your own blanket of warm air. Who would benefit more from this: a human or a shaggy dog?
Why do we get "goose bumps?" (Answer: Skin around the hair follicle is raised as well.)
Pin Prick
A similar activity to this next one was also done in nervous system with differentiation.Use two pins. With the person blindfolded place both pins about an inch apart on the palm of their hand. Ask how many they feel. The answer should be two.
Bring them closer together, about half an inch. Now how many do they feel? (Still two)
Now bring the two points about a quarter to an eighth inch apart. How many do they feel? They will feel only one pin. The two pins are stimulating the same nerve. As far as your brain is concerned, one nerve means one pin is touching it.
Look at the diagram on the skin worksheets to make this explanation more evident to the students.
Now, do it again on the point of the index finger. They probably will feel two distinct points because there are more nerves in the finger tips.
Touch the Tips
Here is another activity that demonstrates the increased sensitivity to the skin on the fingertips.You will need objects with different textures. Here are a few suggestions:
- pin point
- soft, furry cloth like velour or velvet
- rubbery surface like a squishy eraser
Brush each object VERY lightly on the skin over the knuckle. Have them describe it.
Then brush it over the skin of the finger tips. They should have a more definite sense of the objects' texture.
Finger Prints & Lip Prints
Here are some fun skin print ideas:- Use an ink pad to finger print each other.
- Use lipstick to do a lip print.
- Compare foot prints done at birth with their foot prints now.
Learn the major skin parts on the skin worksheets
Epidermis
The epidermis is the top layer of skin that you see. Try to pinch it. You can not pinch just the epidermis with out getting some of the dermis beneath.Dermis
The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the surface of the epidermis. The organs to the skin system are in the dermis.Oil Glands
While these may be the sworn enemy with many teenagers struggling with acne, oil glands really are valuable. They keep the skin moist and healthy. Dry skin is actually more uncomfortable than oily skin.Sweat Glands
Oh, pul leeze, who needs these?Perspiration helps people and animals cool off so they don't get over-heated. It's your own personal air conditioning system.
If you haven't already, now might be a good time to mention the value of underarm deodorant.
Nerves
The nerves in the skin respond to two different types of stimuli. Can your student guess them?(The answer is pressure and temperature.)
You may remember about motor nerves which send messages FROM the brain to the extremeties. No such nerves in the skin. These nerves only send messages TO the brain.
Blood Vessels
Yes, skin has its own blood supply. There are arterioles and venules taking blood to and away from the skin.Subcutaneous Layer
This is a nice way of saying fat. Hey, you have to have some of it you know!Check how much subcutaneous tissue you have beneath the skin of your knuckles. Compare it to the skin in the upper area of your arm.
Now, what would you like like if you didn't have ANY subcutanous fat?
Fat Cells
The fat cells provide insulation to keep the body warm. People who have a lot of body fat will sweat more. It would be similar to having extra layers of blankets.MatchCard Science
How To Use MatchCards
Download the FREE MatchCard Science Instructor's Guide and see how MatchCards can make building their science knowledge base fun.
Human Anatomy Unit Study

Download the entire Human Anatomy Unit Study
12 Science Unit Studies

Chemistry is only one of twelve complete unit studies for kids in 3rd to 8th grade.
Comprehensive objectives, hands-on projects, suggested science fair experiments, and the fun game-like MatchCards keep them interested in learning science. See all twelve MatchCard Science Unit Studies.
About Our Site
Hands-On Learning