Laser Lesson Plans
With our laser lesson plans and FREE download of the laser worksheet, your kids will describe how a laser beam is formed, recognize what a laser is and does, and have fun with our hands on projects.Free Download Below
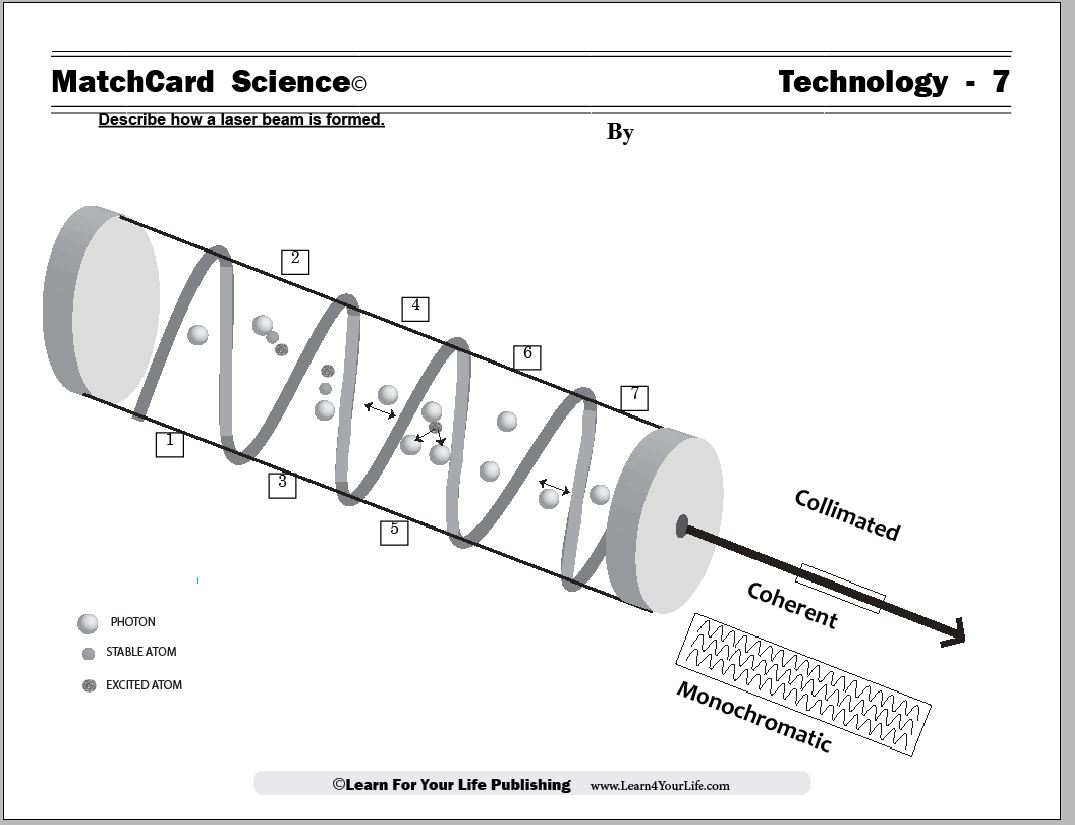

MatchCard Science Laser Worksheett
Objective: Describe how a laser beam is formed.MatchCard: Download below.
On this worksheet students:
- Identify what the acroynm LASER stands form
- Explain the characteristic of a laser beam
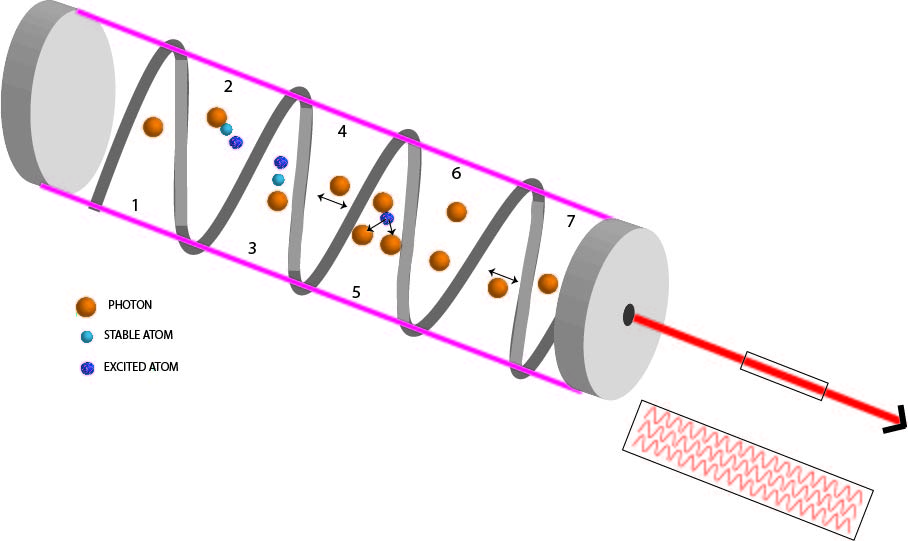
- Describes 7 steps in the formation of a laser beam inside the crystal.
Print the Laser MatchCard


Click image to go to download.
This is MatchCard #7 of the Technology Unit Study. Find more information on MatchCard Science below.
What Is A Laser?
Laser’s have been with us since 1960, though the theories that spawned the creation of lasers go back to Einstein and Max Plank in the earliest years of the 1900’s.A laser is a beam of light that has been amplified. This page will describe what a laser is.
All students can do these activities as well as describe the term “laser” at the top of the MatchCard. The next page includes activities that describe the three characteristics of laser beams; these are for older students. The last activity for your oldest students includes listing the order of events that create a liaser beam.
Light Amplification BY
Stimulated Emission of Radiation
Laser stands for light amplification (by) simulated emission of radiation. Well, that certainly clarified things, right? We can break the phrase down a little further to make some sense of the words.
Stimulated Emission of Radiation
- Stimulate: to excite or activate something
- Emission: release of something (in this case radiation)
- Radiation: electromagnetic radiation
You may remember from Light & Energy Unit Study that electromagnetic radiation is released from the sun as light and other forms of radiation. Now you know that lasers also release radiation - but a whole lot less than the sun!
Now that we have an idea what the stimulated emission of radiation is, what is meant by light amplification?
Light Amplification
- Amplify: to increase
So What Can A Laser Do?
- CD players
- DVDs
- Bar Codes
- Cut hundreds of layers of fabric
- Used in eye surgery
- Telephone signals
- Dental drills
- Car lights
Compare Laser and Flashlight Beams
Have a little fun comparing the laser beam and flashlight beam. Compare:- the diameter of both on a wall
- the clarity (clearness) of the beam
- how far the light beam will shine (may have to do this outside at night.)
Three Characteristics of Lasers
There are 3 primary characteristics of lasers that help to differentiate them from light from a flashlight, light bulb, or the sun. These characteristics of lasers are:- Collimated
- Coherent
- Monochromatic
Collimated
- Collimate: moving in a straight line
- Opposite of collimate: divergence (spreading out)
Compare that to the light beam of the sun or a light bulb which has the characteristics of divergence which means it spreads out in multiple directions. Even the flashlight beam, which is shined in a single direction, has the tendency to diverge. The next characteristic of lasers will explain why the laser remains collimated.
Coherence
- Coherence: consistency
Coherence
- Mono: one in Latin
- Chromatic: color in Greek
Monochromatic Designs
The concept monochromatic will mean something different to a designer than it will to a scientist even though the root of the word is the same. For a scientist, monochromatic means the color is all EXACTLY the same. For a clothes designer or interior designer, monochromatic means you have one family of colors. Such as:- Blue: Light blue, medium blue, dark blue
- Red: pink and scarlet
- Brown: Tan, beige, dark brown
Laser Waterfall
- Laser pointer
- Empty water or soda bottle
How Lasers Are Formed

MatchCard Science
How To Use MatchCards
Download the FREE MatchCard Science Instructor's Guide and see how MatchCards can make building their science knowledge base fun.
12 Science Unit Studies

Chemistry is only one of twelve complete unit studies for kids in 3rd to 8th grade.
Comprehensive objectives, hands-on projects, suggested science fair experiments, and the fun game-like MatchCards keep them interested in learning science. See all twelve MatchCard Science Unit Studies.
About Our Site
Hands-On Learning