Endocrine System Worksheets
Learn Six Major Endocrine Glands and their Hormones
The endocrine system worksheets provide lesson plans from the MatchCard Science Human Anatomy for grades 5 - 8. Identify six major glands and their most important hormones.
Free Download Below

MatchCard Science Endocrine System Worksheets
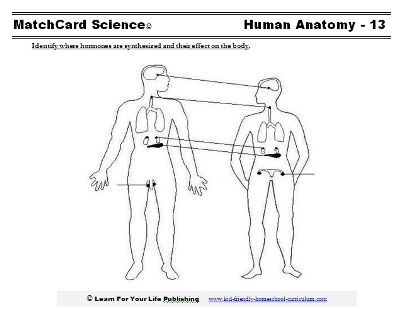
Objective: Identify where hormones are synthesized and their effect on the body.MatchCard: Download below.
MatchCard Information Pieces describe the function and location of synthesis of six hormones. Ideas for projects are listed on the instructor's page and below.
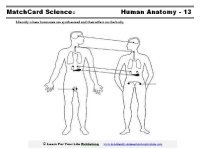
Here's the Endocrine System MatchCard
This is MatchCard #13 of the Human Anatomy Unit Study. Directions for using MatchCards are below.The 1st page is the students' worksheet. The student will match the hormone, the gland, and the function of the hormone to the diagram of the endocrine system.
The 2nd page is the Instructor's Guide with the correct answers.
The 3rd page has the Information Pieces. Student's cut them apart and place them in the correct place on their copy of the Matchcard (first page.)
For more information on how to use the Matchcards, see the MatchCard Science Instructor's Guide.
What is a hormone?
The endocrine system is one of the most complicated systems of human anatomy to understand. It involves the production and secretion of hormones.So what is a hormone? It is a substance produced in a gland in one part of the body that travels through the blood stream to another part of the body.
In some cases, it may affect every cell in the body. Insulin and thyroid hormone are examples of hormones that affect every cell. Others, such as progresterone, have a primary effect on a particular organ.
For this lesson, we are focusing on six endocrine glands and a major hormone of that gland. The number of hormones that are actually in the body are in the hundreds, and for every hormone there are multiple effects. This is a simple introduction to the concept of the endocrine system and its widespread impact on the body.
A Frightening Introduction
Describe this scenario:You are walking all alone late at night. It's hard to see because it is so dark and it feels spooky. All of a sudden, something jumps out of a bush and grabs you.
Describe your reactions. Discuss fear. Discuss the physical effects of fear: involuntary scream, running, wide eyes, hair stands on end, heart races, breathing harder
Let students describe their own scenarios of fear and their reactions.
In the scenario above, imagine the person who jumped out was just a friend. Now you are laughing and no longer afraid. However, it takes a little while to calm down. You still feel jittery and shakey and your heart continues to beat fast.
Why?
The hormone adrenaline was released into your blood system from the adrenal glands on the kidneys. Adrenaline is released in response to fear, stress or anger.
Even though you are no longer scared, the adrenaline is still in your body and causing physical symptoms.
Discuss the fight or flight syndrome: adrenaline helps us fight enemies or flee for safety. It is a valuable hormone produced by a small gland you might not have known existed in your body.
Six Major Hormones
Identify the 6 Hormones on the Endocrine System Worksheets
For each of the six hormones listed on the endocrine system worksheets the student will identify:- The gland where it is synthesized (or made)
- A major hormone of that gland (there are usually more than one)
- What the hormone does
Pituitary Gland
Location: Gland in the brainMajor hormone: Growth Hormone
Function: Causes bones and muscles to grow
Effect of malfunction: Growth restriction
Thyroid Gland
Location: Neck - in front of the pharynx (or throat)Major Hormone: Thyroxin
Function: Increases the rate of metabolism in the cells of the body.
Effect of malfunction: Weight gain or weight loss
Adrenal Gland
Location: Kidneys - below the back ribsMajor Hormone: Adrenaline
Function: Causes the heart rate and breathing to increase
Effect of malfunction: Prolonged stress causes high blood pressure
Pancrease
Location: below stomach in left upper quadrant of the abdomenMajor Hormone: Insulin
Function: Carries glucose into the cells from the blood stream
Malfunction: Diabetes
Testes
Location: Male scrotumMajor Hormone: Testosterone
Function: Causes masculine characteristics and the production of sperm
Malfunction: Infertility
Ovaries
Location: Female pelvis (low abdomen)Major Hormone: Estrogen
Function: Causes female characteristics and helps regulate the menstrual cycle
Other Major Hormone: Progesterone
Function: Prepares the uterine lining for an embryo and causes ovulation
Malfunction: Infertility
Other Ideas for the Study of the Endocrine System for Kids
Memory Game
You can play a matching game like "Memory" with the hormones. Instead of two cards, there are three to a set.Place them face down, and they have to match them.
Hormones and Disease
Hormone deficiences can cause significant disease. Let them choose one hormone and research more about it. In addition to the physical effects, note how it impacts the life of the person as well.Hormone Poster
Choose one of the endocrine glands. List other hormones that it produces.Make a poster of the human body showing the different effects of the hormones from that one gland.
Science Experiment: Sugar, sugar everywhere
This experiment would require you to have access to a home glucose monitoring system which is available to diabetics. This experiment should not be done by a diabetic or someone with a hormone deficiency.Keep track of the calories you eat and your blood glucose one hour after a meal. Draw a chart. What does it show?
Compare a favorite food if you eat at home or eat it at a restaurant. What does that show?
Do some foods cause blood glucose to spike sooner? Can you predict which? Develop a hypothesis and create an experiment to show it.
MatchCard Science
How To Use MatchCards
Download the FREE MatchCard Science Instructor's Guide and see how MatchCards can make building their science knowledge base fun.
Human Anatomy Unit Study

Download the entire Human Anatomy Unit Study
12 Science Unit Studies

Chemistry is only one of twelve complete unit studies for kids in 3rd to 8th grade.
Comprehensive objectives, hands-on projects, suggested science fair experiments, and the fun game-like MatchCards keep them interested in learning science. See all twelve MatchCard Science Unit Studies.
About Our Site
Hands-On Learning